九个JSON.stringify 的秘密,大多数开发人员却不知道
很久以前,我因此在工作中犯下了无法挽回的错误。如果我早点知道,就不会发生这样的悲剧。
理解 JSON.stringify
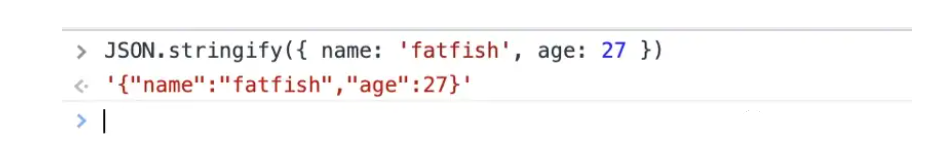
基本上,JSON.stringify 将对象转换为 JSON 字符串。同时,JSON.stringify 有如下规则。
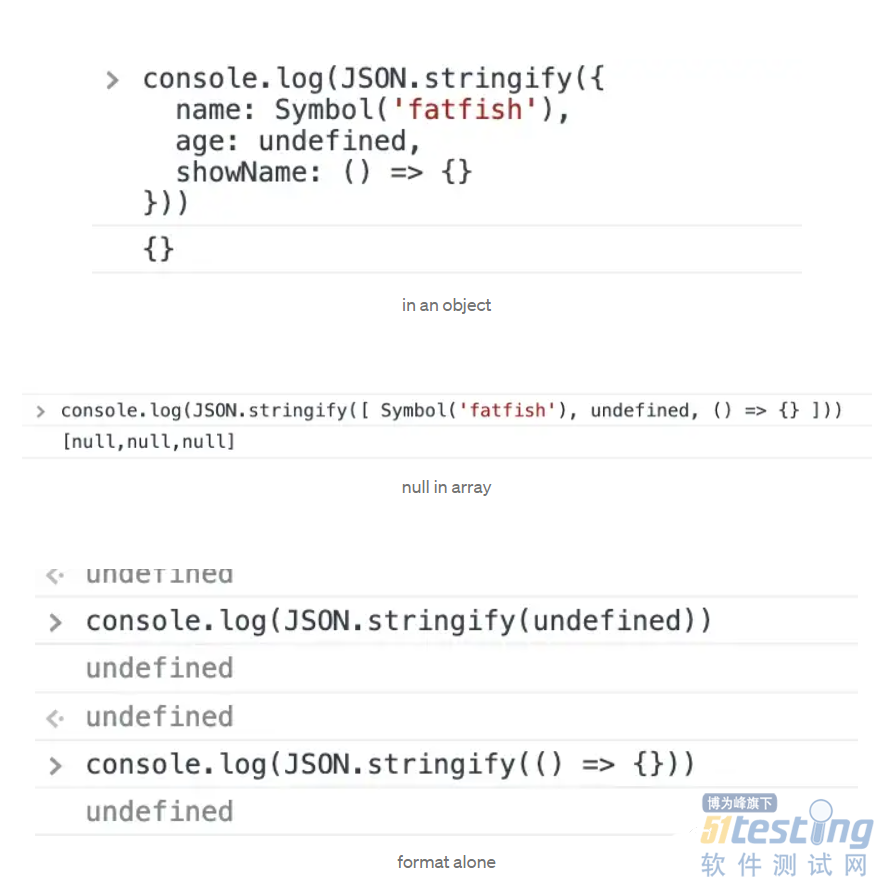
1. undefined、Function 和 Symbol 不是有效的 JSON 值。
如果在转换过程中遇到任何此类值,它们要么被省略(当在对象中找到时),要么更改为 null(当在数组中找到时)。
当传入像 JSON.stringify(function() {}) 或 JSON.stringify(undefined) 这样的“纯”值时,JSON.stringify() 可以返回 undefined。
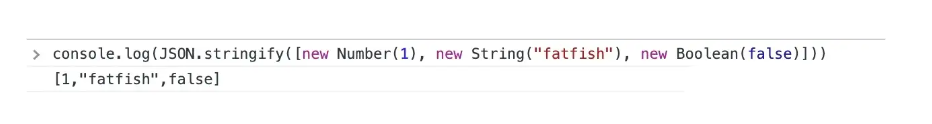
2.Boolean、Number、String对象在字符串化过程中被转换为对应的原始值,符合传统的转换语义。
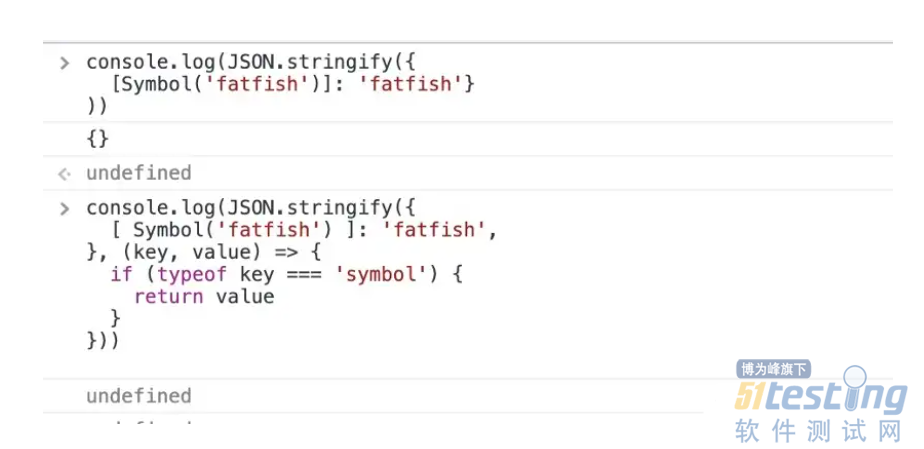
3.所有以符号为键的属性将被完全忽略,即使在使用替换函数时也是如此。
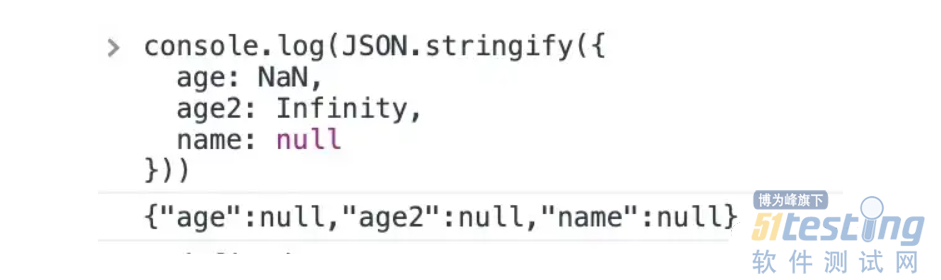
4. 数字 Infinity 和 NaN,以及值 null,都被认为是 null。
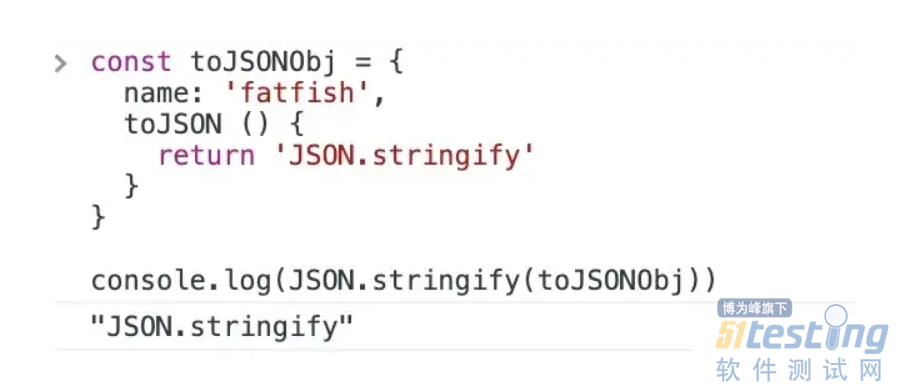
5. 如果该值有一个 toJSON() 方法,它负责定义哪些数据将被序列化。
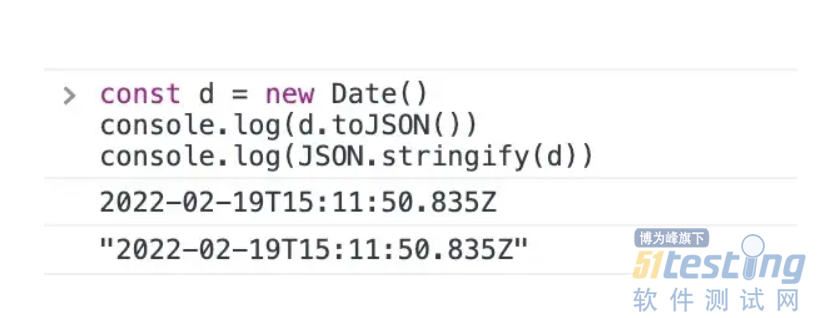
6. Date实例通过返回字符串实现toJSON()函数(同date.toISOString())。
因此,它们被视为字符串。
7. 在包含循环引用的对象上执行此方法会抛出错误。
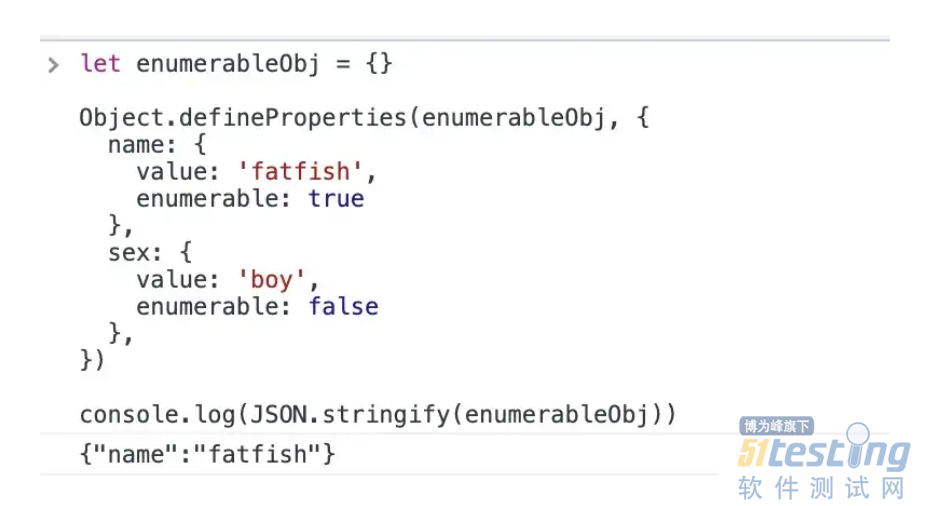
8. 所有其他对象实例(包括 Map、Set、WeakMap 和 WeakSet)将只序列化它们的可枚举属性。
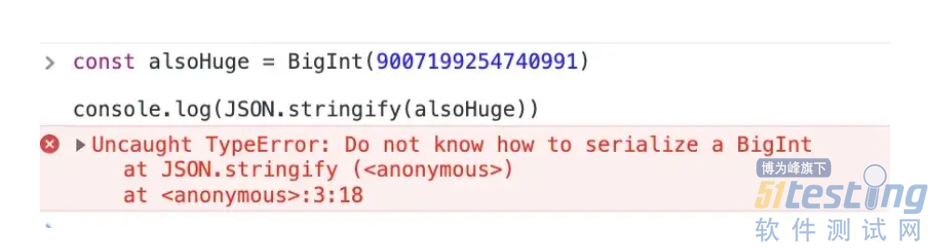
9.尝试转换BigInt类型的值时抛出错误。
自己实现 JSON.stringify
理解功能的最好方法是自己去实现它。 下面我写了一个简单的函数来模拟JSON.stringify。
const jsonstringify = (data) => {
// Check if an object has a circular reference
const isCyclic = (obj) => {
// Use the Set data type to store detected objects
let stackSet = new Set()
let detected = false
const detect = (obj) => {
// If it is not an object type, you can skip it directly
if (obj && typeof obj != 'object') {
return
}
// When the object to be checked already exists in the stackSet, it means that there is a circular reference
if (stackSet.has(obj)) {
return detected = true
}
// Save the current obj as a stackSet
stackSet.add(obj)
for (let key in obj) {
if (obj.hasOwnProperty(key)) {
detect(obj[key])
}
}
// After the level detection is completed, delete the current object to prevent misjudgment
/*
For example:
an object's attribute points to the same reference.
If it is not deleted, it will be regarded as a circular reference
let tempObj = {
name: 'fatfish'
}
let obj4 = {
obj1: tempObj,
obj2: tempObj
}
*/
stackSet.delete(obj)
}
detect(obj)
return detected
}
// 7#:
// Executing this method on an object that contains a circular reference throws an error.
if (isCyclic(data)) {
throw new TypeError('Converting circular structure to JSON')
}
// 9#: An error is thrown when trying to convert a value of type BigInt
// An error is thrown when trying to convert a value of type bigint
if (typeof data === 'bigint') {
throw new TypeError('Do not know how to serialize a BigInt')
}
const type = typeof data
const commonKeys1 = ['undefined', 'function', 'symbol']
const getType = (s) => {
return Object.prototype.toString.call(s).replace(/\[object (.*?)\]/, '$1').toLowerCase()
}
// not an object
if (type !== 'object' || data === null) {
let result = data
// 4#:The numbers Infinity and NaN, as well as the value null, are all considered null.
if ([NaN, Infinity, null].includes(data)) {
result = 'null'
// 1#:undefined, Function, and Symbol are not valid JSON values.
// If any such values are encountered during conversion they are either omitted (when found in an object) or changed to null (when found in an array).
// JSON.stringify() can return undefined when passing in "pure" values like JSON.stringify(function() {}) or JSON.stringify(undefined).
} else if (commonKeys1.includes(type)) {
return undefined
} else if (type === 'string') {
result = '"' + data + '"'
}
return String(result)
} else if (type === 'object') {
// 5#: If the value has a toJSON() method, it's responsible to define what data will be serialized.
// 6#: The instances of Date implement the toJSON() function by returning a string (the same as date.toISOString()).
// Thus, they are treated as strings.
if (typeof data.toJSON === 'function') {
return jsonstringify(data.toJSON())
} else if (Array.isArray(data)) {
let result = data.map((it) => {
// 1#: If any such values are encountered during conversion they are either omitted (when found in an object) or changed to null (when found in an array).
return commonKeys1.includes(typeof it) ? 'null' : jsonstringify(it)
})
return `[${result}]`.replace(/'/g, '"')
} else {
// 2#:Boolean, Number, and String objects are converted to the corresponding primitive values during stringification, in accord with the traditional conversion semantics.
if (['boolean', 'number'].includes(getType(data))) {
return String(data)
} else if (getType(data) === 'string') {
return '"' + data + '"'
} else {
let result = []
// 8#: All the other Object instances (including Map, Set, WeakMap, and WeakSet) will have only their enumerable properties serialized.
Object.keys(data).forEach((key) => {
// 3#: All Symbol-keyed properties will be completely ignored, even when using the replacer function.
if (typeof key !== 'symbol') {
const value = data[key]
// 1#: undefined, Function, and Symbol are not valid JSON values.
if (!commonKeys1.includes(typeof value)) {
result.push(`"${key}":${jsonstringify(value)}`)
}
}
})
return `{${result}}`.replace(/'/, '"')
}
}
}
}
还有一个测试
// 1. Test basic features
console.log(jsonstringify(undefined)) // undefined
console.log(jsonstringify(() => { })) // undefined
console.log(jsonstringify(Symbol('fatfish'))) // undefined
console.log(jsonstringify((NaN))) // null
console.log(jsonstringify((Infinity))) // null
console.log(jsonstringify((null))) // null
console.log(jsonstringify({
name: 'fatfish',
toJSON() {
return {
name: 'fatfish2',
sex: 'boy'
}
}
}))
// {"name":"fatfish2","sex":"boy"}
// 2. Compare with native JSON.stringify
console.log(jsonstringify(null) === JSON.stringify(null));
// true
console.log(jsonstringify(undefined) === JSON.stringify(undefined));
// true
console.log(jsonstringify(false) === JSON.stringify(false));
// true
console.log(jsonstringify(NaN) === JSON.stringify(NaN));
// true
console.log(jsonstringify(Infinity) === JSON.stringify(Infinity));
// true
let str = "fatfish";
console.log(jsonstringify(str) === JSON.stringify(str));
// true
let reg = new RegExp("\w");
console.log(jsonstringify(reg) === JSON.stringify(reg));
// true
let date = new Date();
console.log(jsonstringify(date) === JSON.stringify(date));
// true
let sym = Symbol('fatfish');
console.log(jsonstringify(sym) === JSON.stringify(sym));
// true
let array = [1, 2, 3];
console.log(jsonstringify(array) === JSON.stringify(array));
// true
let obj = {
name: 'fatfish',
age: 18,
attr: ['coding', 123],
date: new Date(),
uni: Symbol(2),
sayHi: function () {
console.log("hello world")
},
info: {
age: 16,
intro: {
money: undefined,
job: null
}
},
pakingObj: {
boolean: new Boolean(false),
string: new String('fatfish'),
number: new Number(1),
}
}
console.log(jsonstringify(obj) === JSON.stringify(obj))
// true
console.log((jsonstringify(obj)))
// {"name":"fatfish","age":18,"attr":["coding",123],"date":"2021-10-06T14:59:58.306Z","info":{"age":16,"intro":{"job":null}},"pakingObj":{"boolean":false,"string":"fatfish","number":1}}
console.log(JSON.stringify(obj))
// {"name":"fatfish","age":18,"attr":["coding",123],"date":"2021-10-06T14:59:58.306Z","info":{"age":16,"intro":{"job":null}},"pakingObj":{"boolean":false,"string":"fatfish","number":1}}
// 3. Test traversable objects
let enumerableObj = {}
Object.defineProperties(enumerableObj, {
name: {
value: 'fatfish',
enumerable: true
},
sex: {
value: 'boy',
enumerable: false
},
})
console.log(jsonstringify(enumerableObj))
// {"name":"fatfish"}
// 4. Testing circular references and Bigint
let obj1 = { a: 'aa' }
let obj2 = { name: 'fatfish', a: obj1, b: obj1 }
obj2.obj = obj2
console.log(jsonstringify(obj2))
// TypeError: Converting circular structure to JSON
console.log(jsonStringify(BigInt(1)))
// TypeError: Do not know how to serialize a BigInt
// 1. Test basic featuresconsole.log(jsonstringify(undefined)) // undefined console.log(jsonstringify(() { })) // undefinedconsole.log(jsonstringify(Symbol('fatfish'))) // undefinedconsole.log(jsonstringify((NaN))) // nullconsole.log(jsonstringify((Infinity))) // nullconsole.log(jsonstringify((null))) // nullconsole.log(jsonstringify({name: 'fatfish', toJSON() { return {name: 'fatfish2',sex: 'boy' } }}))// {"name":"fatfish2","sex":"boy"}
// 2. Compare with native JSON.stringifyconsole.log(jsonstringify(null) === JSON.stringify(null));// trueconsole.log(jsonstringify(undefined) === JSON.stringify(undefined));// trueconsole.log(jsonstringify(false) === JSON.stringify(false));// trueconsole.log(jsonstringify(NaN) === JSON.stringify(NaN));// trueconsole.log(jsonstringify(Infinity) === JSON.stringify(Infinity));// truelet str = "fatfish";console.log(jsonstringify(str) === JSON.stringify(str));// truelet reg = new RegExp("\w");console.log(jsonstringify(reg) === JSON.stringify(reg));// truelet date = new Date();console.log(jsonstringify(date) === JSON.stringify(date));// truelet sym = Symbol('fatfish');console.log(jsonstringify(sym) === JSON.stringify(sym));// truelet array = [1, 2, 3];console.log(jsonstringify(array) === JSON.stringify(array));// truelet obj = {name: 'fatfish',age: 18,attr: ['coding', 123],date: new Date(),uni: Symbol(2),sayHi: function () { console.log("hello world") },info: {age: 16,intro: {money: undefined,job: null } },pakingObj: {boolean: new Boolean(false),string: new String('fatfish'),number: new Number(1), }}console.log(jsonstringify(obj) === JSON.stringify(obj)) // trueconsole.log((jsonstringify(obj)))// {"name":"fatfish","age":18,"attr":["coding",123],"date":"2021-10-06T14:59:58.306Z","info":{"age":16,"intro":{"job":null}},"pakingObj":{"boolean":false,"string":"fatfish","number":1}}console.log(JSON.stringify(obj))// {"name":"fatfish","age":18,"attr":["coding",123],"date":"2021-10-06T14:59:58.306Z","info":{"age":16,"intro":{"job":null}},"pakingObj":{"boolean":false,"string":"fatfish","number":1}}
// 3. Test traversable objectslet enumerableObj = {}
Object.defineProperties(enumerableObj, {name: {value: 'fatfish',enumerable: true },sex: {value: 'boy',enumerable: false },})
console.log(jsonstringify(enumerableObj))// {"name":"fatfish"}
// 4. Testing circular references and Bigint
let obj1 = { a: 'aa' }let obj2 = { name: 'fatfish', a: obj1, b: obj1 }obj2.obj = obj2
console.log(jsonstringify(obj2))// TypeError: Converting circular structure to JSONconsole.log(jsonStringify(BigInt(1)))// TypeError: Do not know how to serialize a BigInt
最后
以上就是我今天跟你分享的全部内容,希望你能从今天的文章中学到新的知识。
相关阅读:
- 用于前端开发的 React 或 Angular (liqianqian1116, 2022-11-08)
- 如何避免由 Web 字体引起的布局偏移 (liqianqian1116, 2022-11-17)
- 前端如何实现新手引导功能? (liqianqian1116, 2022-11-28)
- 有哪些方法可以快速把网站都变成灰色? (大椿菜, 2022-12-12)
- 前端错误监控-Sentry自动捕获前端应用异常原理 (liqianqian1116, 2022-12-08)
- 从这个API能看到整个前端的缩影 (liqianqian1116, 2022-12-19)
- 像书写代码一样撰写文档 (liqianqian1116, 2022-12-22)
- Go 框架 Gin 怎么实现允许前端跨域请求? (liqianqian1116, 2022-12-27)
- 敏捷是知与行的功夫 (liqianqian1116, 2023-1-17)
标题搜索
我的存档
数据统计
- 访问量: 245349
- 日志数: 939
- 建立时间: 2020-08-11
- 更新时间: 2024-04-12