整理了27个Python人工智能库,一定要收藏(1)
1、Numpy
NumPy(Numerical Python)是 Python的一个扩展程序库,支持大量的维度数组与矩阵运算,此外也针对数组运算提供大量的数学函数库,Numpy底层使用C语言编写,数组中直接存储对象,而不是存储对象指针,所以其运算效率远高于纯Python代码。
我们可以在示例中对比下纯Python与使用Numpy库在计算列表sin值的速度对比:
import numpy as np
import math
import random
import time
start = time.time()
for i in range(10):
list_1 = list(range(1,10000))
for j in range(len(list_1)):
list_1[j] = math.sin(list_1[j])
print("使用纯Python用时{}s".format(time.time()-start))
start = time.time()
for i in range(10):
list_1 = np.array(np.arange(1,10000))
list_1 = np.sin(list_1)
print("使用Numpy用时{}s".format(time.time()-start))
从如下运行结果,可以看到使用 Numpy 库的速度快于纯 Python 编写的代码:
使用纯Python用时0.017444372177124023s
使用Numpy用时0.001619577407836914s
2、OpenCV
OpenCV 是一个的跨平台计算机视觉库,可以运行在 Linux、Windows 和 Mac OS 操作系统上。它轻量级而且高效——由一系列 C 函数和少量 C++ 类构成,同时也提供了 Python 接口,实现了图像处理和计算机视觉方面的很多通用算法。
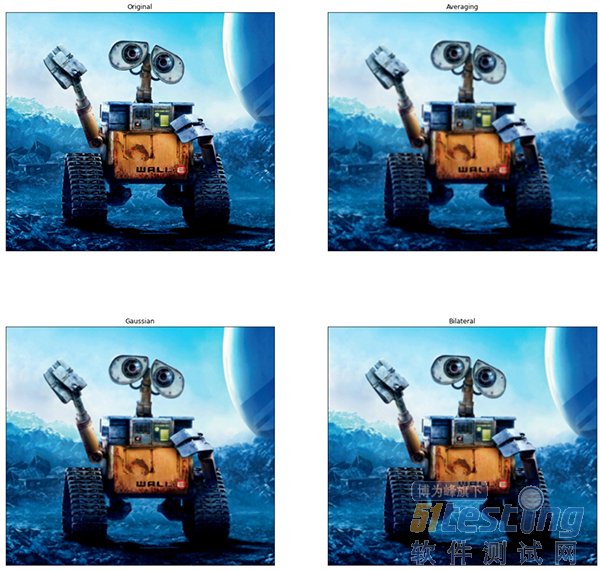
下面代码尝试使用一些简单的滤镜,包括图片的平滑处理、高斯模糊等:
import numpy as np
import cv2 as cv
from matplotlib import pyplot as plt
img = cv.imread('h89817032p0.png')
kernel = np.ones((5,5),np.float32)/25
dst = cv.filter2D(img,-1,kernel)
blur_1 = cv.GaussianBlur(img,(5,5),0)
blur_2 = cv.bilateralFilter(img,9,75,75)
plt.figure(figsize=(10,10))
plt.subplot(221),plt.imshow(img[:,:,::-1]),plt.title('Original')
plt.xticks([]), plt.yticks([])
plt.subplot(222),plt.imshow(dst[:,:,::-1]),plt.title('Averaging')
plt.xticks([]), plt.yticks([])
plt.subplot(223),plt.imshow(blur_1[:,:,::-1]),plt.title('Gaussian')
plt.xticks([]), plt.yticks([])
plt.subplot(224),plt.imshow(blur_1[:,:,::-1]),plt.title('Bilateral')
plt.xticks([]), plt.yticks([])
plt.show()
OpenCV
3、Scikit-image
scikit-image是基于scipy的图像处理库,它将图片作为numpy数组进行处理。
例如,可以利用scikit-image改变图片比例,scikit-image提供了rescale、resize以及downscale_local_mean等函数。
from skimage import data, color, io
from skimage.transform import rescale, resize, downscale_local_mean
image = color.rgb2gray(io.imread('h89817032p0.png'))
image_rescaled = rescale(image, 0.25, anti_aliasing=False)
image_resized = resize(image, (image.shape[0] // 4, image.shape[1] // 4),
anti_aliasing=True)
image_downscaled = downscale_local_mean(image, (4, 3))
plt.figure(figsize=(20,20))
plt.subplot(221),plt.imshow(image, cmap='gray'),plt.title('Original')
plt.xticks([]), plt.yticks([])
plt.subplot(222),plt.imshow(image_rescaled, cmap='gray'),plt.title('Rescaled')
plt.xticks([]), plt.yticks([])
plt.subplot(223),plt.imshow(image_resized, cmap='gray'),plt.title('Resized')
plt.xticks([]), plt.yticks([])
plt.subplot(224),plt.imshow(image_downscaled, cmap='gray'),plt.title('Downscaled')
plt.xticks([]), plt.yticks([])
plt.show()
Scikit-image
4、PIL
Python Imaging Library(PIL) 已经成为 Python 事实上的图像处理标准库了,这是由于,PIL 功能非常强大,但API却非常简单易用。
但是由于PIL仅支持到 Python 2.7,再加上年久失修,于是一群志愿者在 PIL 的基础上创建了兼容的版本,名字叫 Pillow,支持最新 Python 3.x,又加入了许多新特性,因此,我们可以跳过 PIL,直接安装使用 Pillow。
5、Pillow
使用 Pillow 生成字母验证码图片:
from PIL import Image, ImageDraw, ImageFont, ImageFilter
import random
# 随机字母:
def rndChar():
return chr(random.randint(65, 90))
# 随机颜色1:
def rndColor():
return (random.randint(64, 255), random.randint(64, 255), random.randint(64, 255))
# 随机颜色2:
def rndColor2():
return (random.randint(32, 127), random.randint(32, 127), random.randint(32, 127))
# 240 x 60:
width = 60 * 6
height = 60 * 6
image = Image.new('RGB', (width, height), (255, 255, 255))
# 创建Font对象:
font = ImageFont.truetype('/usr/share/fonts/wps-office/simhei.ttf', 60)
# 创建Draw对象:
draw = ImageDraw.Draw(image)
# 填充每个像素:
for x in range(width):
for y in range(height):
draw.point((x, y), fill=rndColor())
# 输出文字:
for t in range(6):
draw.text((60 * t + 10, 150), rndChar(), font=font, fill=rndColor2())
# 模糊:
image = image.filter(ImageFilter.BLUR)
image.save('code.jpg', 'jpeg')
验证码
6、SimpleCV
SimpleCV 是一个用于构建计算机视觉应用程序的开源框架。使用它,可以访问高性能的计算机视觉库,如 OpenCV,而不必首先了解位深度、文件格式、颜色空间、缓冲区管理、特征值或矩阵等术语。但其对于 Python3 的支持很差很差,在 Python3.7 中使用如下代码:
from SimpleCV import Image, Color, Display
# load an image from imgur
img = Image('http://i.imgur.com/lfAeZ4n.png')
# use a keypoint detector to find areas of interest
feats = img.findKeypoints()
# draw the list of keypoints
feats.draw(color=Color.RED)
# show the resulting image.
img.show()
# apply the stuff we found to the image.
output = img.applyLayers()
# save the results.
output.save('juniperfeats.png')
会报如下错误,因此不建议在 Python3 中使用:
SyntaxError: Missing parentheses in call to 'print'. Did you mean print('unit test')
7、Mahotas
Mahotas 是一个快速计算机视觉算法库,其构建在 Numpy 之上,目前拥有超过100种图像处理和计算机视觉功能,并在不断增长。
使用 Mahotas 加载图像,并对像素进行操作:
import numpy as np
import mahotas
import mahotas.demos
from mahotas.thresholding import soft_threshold
from matplotlib import pyplot as plt
from os import path
f = mahotas.demos.load('lena', as_grey=True)
f = f[128:,128:]
plt.gray()
# Show the data:
print("Fraction of zeros in original image: {0}".format(np.mean(f==0)))
plt.imshow(f)
plt.show()
Mahotas
8、Ilastik
Ilastik 能够给用户提供良好的基于机器学习的生物信息图像分析服务,利用机器学习算法,轻松地分割,分类,跟踪和计数细胞或其他实验数据。大多数操作都是交互式的,并不需要机器学习专业知识。
9、Scikit-learn
Scikit-learn 是针对 Python 编程语言的免费软件机器学习库。它具有各种分类,回归和聚类算法,包括支持向量机,随机森林,梯度提升,k均值和 DBSCAN 等多种机器学习算法。
使用Scikit-learn实现KMeans算法:
import time
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from sklearn.cluster import MiniBatchKMeans, KMeans
from sklearn.metrics.pairwise import pairwise_distances_argmin
from sklearn.datasets import make_blobs
# Generate sample data
np.random.seed(0)
batch_size = 45
centers = [[1, 1], [-1, -1], [1, -1]]
n_clusters = len(centers)
X, labels_true = make_blobs(n_samples=3000, centers=centers, cluster_std=0.7)
# Compute clustering with Means
k_means = KMeans(init='k-means++', n_clusters=3, n_init=10)
t0 = time.time()
k_means.fit(X)
t_batch = time.time() - t0
# Compute clustering with MiniBatchKMeans
mbk = MiniBatchKMeans(init='k-means++', n_clusters=3, batch_size=batch_size,
n_init=10, max_no_improvement=10, verbose=0)
t0 = time.time()
mbk.fit(X)
t_mini_batch = time.time() - t0
# Plot result
fig = plt.figure(figsize=(8, 3))
fig.subplots_adjust(left=0.02, right=0.98, bottom=0.05, top=0.9)
colors = ['#4EACC5', '#FF9C34', '#4E9A06']
# We want to have the same colors for the same cluster from the
# MiniBatchKMeans and the KMeans algorithm. Let's pair the cluster centers per
# closest one.
k_means_cluster_centers = k_means.cluster_centers_
order = pairwise_distances_argmin(k_means.cluster_centers_,
mbk.cluster_centers_)
mbk_means_cluster_centers = mbk.cluster_centers_[order]
k_means_labels = pairwise_distances_argmin(X, k_means_cluster_centers)
mbk_means_labels = pairwise_distances_argmin(X, mbk_means_cluster_centers)
# KMeans
for k, col in zip(range(n_clusters), colors):
my_members = k_means_labels == k
cluster_center = k_means_cluster_centers[k]
plt.plot(X[my_members, 0], X[my_members, 1], 'w',
markerfacecolor=col, marker='.')
plt.plot(cluster_center[0], cluster_center[1], 'o', markerfacecolor=col,
markeredgecolor='k', markersize=6)
plt.title('KMeans')
plt.xticks(())
plt.yticks(())
plt.show()
KMeans
10、SciPy
SciPy 库提供了许多用户友好和高效的数值计算,如数值积分、插值、优化、线性代数等。
SciPy 库定义了许多数学物理的特殊函数,包括椭圆函数、贝塞尔函数、伽马函数、贝塔函数、超几何函数、抛物线圆柱函数等等。
from scipy import special
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import numpy as np
def drumhead_height(n, k, distance, angle, t):
kth_zero = special.jn_zeros(n, k)[-1]
return np.cos(t) * np.cos(n*angle) * special.jn(n, distance*kth_zero)
theta = np.r_[0:2*np.pi:50j]
radius = np.r_[0:1:50j]
x = np.array([r * np.cos(theta) for r in radius])
y = np.array([r * np.sin(theta) for r in radius])
z = np.array([drumhead_height(1, 1, r, theta, 0.5) for r in radius])
fig = plt.figure()
ax = fig.add_axes(rect=(0, 0.05, 0.95, 0.95), projection='3d')
ax.plot_surface(x, y, z, rstride=1, cstride=1, cmap='RdBu_r', vmin=-0.5, vmax=0.5)
ax.set_xlabel('X')
ax.set_ylabel('Y')
ax.set_xticks(np.arange(-1, 1.1, 0.5))
ax.set_yticks(np.arange(-1, 1.1, 0.5))
ax.set_zlabel('Z')
plt.show()
SciPy
相关阅读:
- 四个Python项目管理与构建工具,建议收藏! (liqianqian1116, 2022-8-23)
- 有用但不为大家所熟知的 Java 特性 (liqianqian1116, 2022-8-16)
- Python 开发桌面小工具,让代码替我们干重复的工作! (liqianqian1116, 2022-8-15)
- 太全了!用Python操作MySQL的使用教程集锦! (liqianqian1116, 2022-8-16)
- 抛弃for循环,让Python代码更pythonic ! (liqianqian1116, 2022-8-22)
- 太牛了,用Python实现服务部署自动化! (liqianqian1116, 2022-8-19)
标题搜索
我的存档
数据统计
- 访问量: 224797
- 日志数: 864
- 建立时间: 2020-08-11
- 更新时间: 2024-02-06