什么是单元测试
单元测试又称模块测试,是针对软件设计的最小单位(模块)就行正确性的校验的测试,检查每个程序模块是否实现了规定的功能,保证其正常工作。
测试的重点:系统模块、方法的逻辑正确性。
和集成测试不同,单元测试应该具备如下特点:
1. 尽可能简短不重复。
2. 执行速度快,因为单元测试几乎可以一直运行,所以对于一些数据库、文件操作等一定要加快速度,可以采用mock的方式。
3. 具有100%的确定性,不能某几次可以执行成功,某几次执行失败。
我们在企业开发中,很多大公司都是要求单测到达一定的比率才能提交代码,单测能够保证我们写的逻辑代码符合我们的预期,并且在后续的维护中都能通过单测来验证我们的修改有没有把原有的代码逻辑改错。
虽然会花费我们额外10%的时间去做单测,但是收益率还是值得的,作为一个开发,我认为我们本就该进行完整的自测后才移交给测试同学。
单元测试入门
先写一个简单的单测例子:测试一个求两个set集合交集的方法
引入依赖
<dependency>
<groupId>org.mockito</groupId>
<artifactId>mockito-core</artifactId>
<version>4.3.1</version>
<scope>test</scope>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.junit.jupiter</groupId>
<artifactId>junit-jupiter</artifactId>
<version>5.8.2</version>
<scope>test</scope>
</dependency>
被测试方法
/**
* 获取交集
* @param set1
* @param set2
* @return
*/
public Set<Integer> getIntersection(Set<Integer> set1,Set<Integer> set2){
set1.retainAll(set2);
return set2;
}
生成测试方法
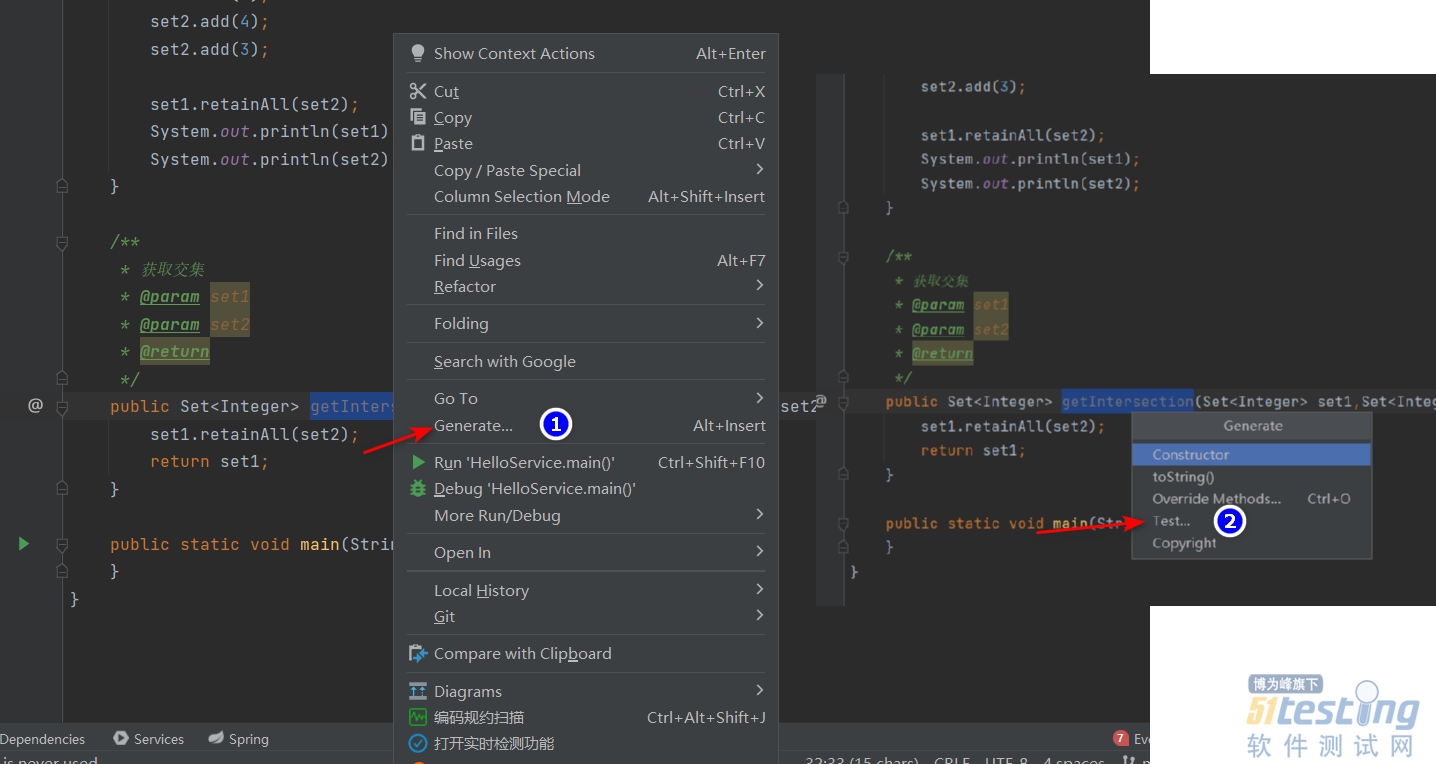
我们可以通过IDEA的自动生成功能来生成测试方法。
它会在test目录下的同包名下生成一个测试类。
我们编写测试逻辑
class HelloServiceTest {
@Test
void getIntersection() {
//生成mock类
HelloService helloService = Mockito.mock(HelloService.class);
//调用mock类的getIntersection方法时调用真实方法
Mockito.when(helloService.getIntersection(Mockito.anySet(),Mockito.anySet())).thenCallRealMethod();
Set<Integer> set1=new HashSet<>();
set1.add(1);
set1.add(2);
set1.add(3);
Set<Integer> set2=new HashSet<>();
set2.add(5);
set2.add(4);
set2.add(3);
Set<Integer> intersection = helloService.getIntersection(set1, set2);
Set<Integer> set3=new HashSet<>();
set3.add(3);
//断言,判断方法结果是否和我们预想的一致
Assertions.assertEquals(intersection,set3);
}
}
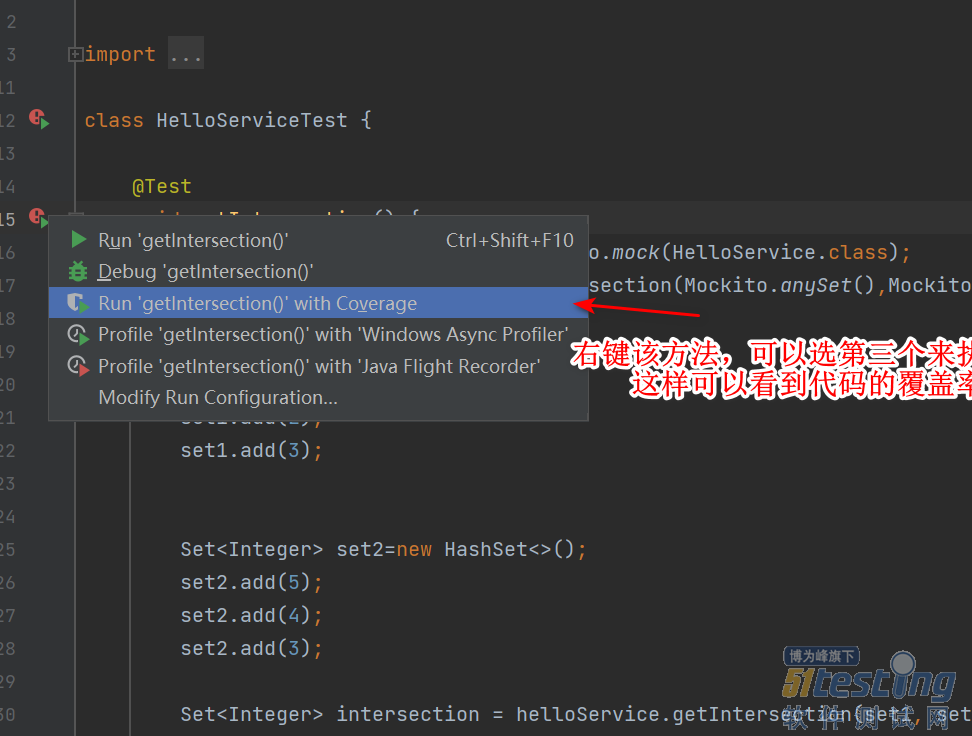
运行
运行结果:
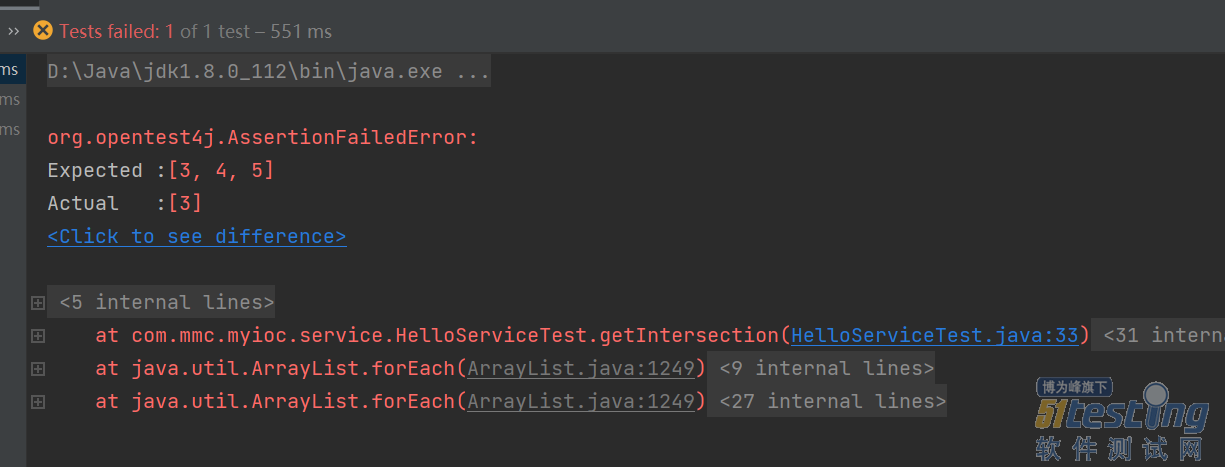
运行完后发现断言异常,这样就能检查出我们之前写的代码不对,去检查了下,发现了问题,改正代码后重试。
public Set<Integer> getIntersection(Set<Integer> set1,Set<Integer> set2){
set1.retainAll(set2);
return set1;
}
常用方法
构建测试对象
mock方法
方法1
HelloService helloService = Mockito.mock(HelloService.class);
方法2:
使用注解
@Mock
private HelloService helloService;
@Test
void getIntersection() {
//使用@Mock,需要加下面这行代码
MockitoAnnotations.openMocks(this);
Mockito.when(helloService.getIntersection(Mockito.anySet(),Mockito.anySet())).thenCallRealMethod();
...
}
mock出来的对象,要指定方法的返回,否则只是返回默认值,不会执行真正的方法的实现。
直接使用new 方法构建对象
HelloService helloService = new HelloService();
使用@Spy注解
@Spy
private HelloService helloService;
使用@Spy注解的对象,在执行的时候会调用真实的方法。
上面都是简单的一级对象的构建,如果被测试的对象里面还要对象依赖怎么办呢?
构建依赖的测试对象
如这个方法:
@Setter
public class HelloService {
private HelloDao helloDao;
public String hello(){
return helloDao.hello()+" xiaowang";
}
}
mock + set
HelloService helloService=new HelloService();
HelloDao helloDao = Mockito.mock(HelloDao.class);
helloService.setHelloDao(helloDao);
@InjectMocks
使用@InjectMocks可以将mock出的依赖对象注入到它标注的测试对象中
@InjectMocks
private HelloService helloService;
@Mock
private HelloDao helloDao;
上面的例子中,将helloDao注入到了helloService中
构建静态对象
需要修改依赖
<!-- <dependency>-->
<!-- <groupId>org.mockito</groupId>-->
<!-- <artifactId>mockito-core</artifactId>-->
<!-- <version>4.3.1</version>-->
<!-- <scope>test</scope>-->
<!-- </dependency>-->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.mockito</groupId>
<artifactId>mockito-inline</artifactId>
<version>4.3.1</version>
<scope>test</scope>
</dependency>
MockedStatic<JsonUtils> tMockedStatic = Mockito.mockStatic(JsonUtils.class);
因为静态方法mock了之后,在整个线程中都是生效的,如果需要隔离的话,可以使用try-with-resources来写。
区别如下:
行为规定(打桩)
接下来我们学习方法的行为规定,因为mock出来的对象默认是不执行真实方法的,需要我们指定。
doReturn
Mockito.doReturn("hello").when(helloDao).hello();
thenReturn
Mockito.when(helloDao.hello()).thenReturn("hello");
thenAnswer
这种方式可以灵活的返回,比如根据参数的不同返回不同的值
Mockito.when(helloDao.hello(Mockito.anyString())).thenAnswer( invocation->{
String param = invocation.getArgument(0);
if(param.equals("w")){
return "wang";
}else {
return "li";
}
});
mock异常
有时候需要测试方法异常的时候对整个方法体的影响。
Mockito.when(helloDao.hello(Mockito.anyString())).thenThrow(NullPointerException.class);
断言
我们执行完测试方法后,就需要对结果进行验证比对,来证明我们的方法的正确性。
Assertions.assertEquals
Assertions.assertEquals(hello,"hello xiaowang");
Assertions.assertTrue
Assertions.assertTrue(hello.equals("hello xiaowang"));
Assertions.assertThrows
异常断言,判断是否是预期的异常
Assertions.assertThrows(NullPointerException.class,()->{
helloDao.hello();
});
使用Verify断言执行次数
Mockito.verify(helloDao,Mockito.times(1)).hello();
番外
另外还有两个注解,@BeforeEach和@AfterEach,顾名思义,一个是在test方法执行前执行,一个是在test方法执行后执行。
@BeforeEach
public void before(){
System.out.println("before");
}
@AfterEach
public void after(){
System.out.println("after");
}
另外推荐两款比较好用的单测生成插件 TestMe 和Diffblue。
本文内容不用于商业目的,如涉及知识产权问题,请权利人联系51Testing小编(021-64471599-8017),我们将立即处理