一、关于Robolectric3.0
文章中的所有代码在此:https://github.com/geniusmart/LoveUT,由于Robolectric3.0和3.1版本(包括后续3.x版本)差异不小,该工程中包含这两个版本对应的测试用例 Demo 。
那么如何测试自己写的代码?点点界面,测测功能固然是一种方式,但是如果能留下一段一劳永逸的测试代码,让代码测试代码,岂不两全其美?所以,写好单元测试,爱惜自己的代码,爱惜颜值高的QA妹纸,爱惜有价值的产品(没价值的、政治性的、屁股决定脑袋的产品滚粗),人人有责!
对于Android app来说,写起单元测试来瞻前顾后,一方面单元测试需要运行在模拟器上或者真机上,麻烦而且缓慢,另一方面,一些依赖Android SDK的对象(如Activity,TextView等)的测试非常头疼,Robolectric可以解决此类问题,它的设计思路便是通过实现一套JVM能运行的Android代码,从而做到脱离Android环境进行测试。本文对Robolectric3.0做了简单介绍,并列举了如何对Android的组件和常见功能进行测试的示例。
二、环境搭建
Gradle配置
在build.gradle中配置如下依赖关系:
| testCompile "org.robolectric:robolectric:3.0" |
通过注解配置TestRunner
@RunWith(RobolectricGradleTestRunner.class) @Config(constants = BuildConfig.class) public class SampleActivityTest { } |
Android Studio的配置
在Build Variants面板中,将Test Artifact切换成Unit Tests模式(注:新版本的as已经不需要做这项配置),如下图:
配置Test Artifact
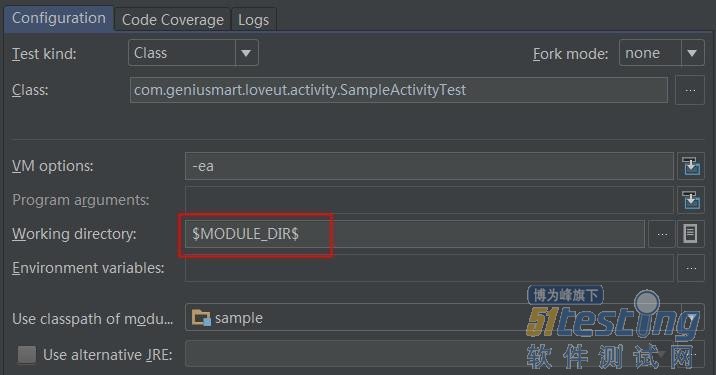
working directory 设置为$MODULE_DIR$
如果在测试过程遇见如下问题,解决的方式就是设置working directory的值:
| java.io.FileNotFoundException: build\intermediates\bundles\debug\AndroidManifest.xml (系统找不到指定的路径。) |
设置方法如下图所示:
Edit Configurations
Working directory的配置
更多环境配置可以参考官方网站。
三、Activity的测试
1、创建Activity实例
@Test public void testActivity() { SampleActivity sampleActivity = Robolectric.setupActivity(SampleActivity.class); assertNotNull(sampleActivity); assertEquals(sampleActivity.getTitle(), "SimpleActivity"); } |
2、生命周期
@Test public void testLifecycle() { ActivityController<SampleActivity> activityController = Robolectric.buildActivity(SampleActivity.class).create().start(); Activity activity = activityController.get(); TextView textview = (TextView) activity.findViewById(R.id.tv_lifecycle_value); assertEquals("onCreate",textview.getText().toString()); activityController.resume(); assertEquals("onResume", textview.getText().toString()); activityController.destroy(); assertEquals("onDestroy", textview.getText().toString()); } |
3、跳转
@Test public void testStartActivity() { //按钮点击后跳转到下一个Activity forwardBtn.performClick(); Intent expectedIntent = new Intent(sampleActivity, LoginActivity.class); Intent actualIntent = ShadowApplication.getInstance().getNextStartedActivity(); assertEquals(expectedIntent, actualIntent); } |
注:Robolectric 3.1 之后,不建议用 Intent.equals() 的方式来比对两个 Intent ,因此以上代码将无法正常执行。目前建议用类似代码来断言:
| assertEquals(expectedIntent.getComponent(), actualIntent.getComponent()); |
当然,Intent 有很多属性,如果需要分别断言的话比较麻烦,因此可以用一些第三方库,比如 assertj-android 的工具类 IntentAssert。
4、UI组件状态
@Test public void testViewState(){ CheckBox checkBox = (CheckBox) sampleActivity.findViewById(R.id.checkbox); Button inverseBtn = (Button) sampleActivity.findViewById(R.id.btn_inverse); assertTrue(inverseBtn.isEnabled()); checkBox.setChecked(true); //点击按钮,CheckBox反选 inverseBtn.performClick(); assertTrue(!checkBox.isChecked()); inverseBtn.performClick(); assertTrue(checkBox.isChecked()); } |
5、Dialog
@Test public void testDialog(){ //点击按钮,出现对话框 dialogBtn.performClick(); AlertDialog latestAlertDialog = ShadowAlertDialog.getLatestAlertDialog(); assertNotNull(latestAlertDialog); } |
6、Toast
@Test public void testToast(){ //点击按钮,出现吐司 toastBtn.performClick(); assertEquals(ShadowToast.getTextOfLatestToast(),"we love UT"); } |
7、Fragment的测试
如果使用support的Fragment,需添加以下依赖
| testCompile "org.robolectric:shadows-support-v4:3.0" |
shadow-support包提供了将Fragment主动添加到Activity中的方法:SupportFragmentTestUtil.startFragment(),简易的测试代码如下
@Test
public void testFragment(){
SampleFragment sampleFragment = new SampleFragment();
//此api可以主动添加Fragment到Activity中,因此会触发Fragment的onCreateView()
SupportFragmentTestUtil.startFragment(sampleFragment);
assertNotNull(sampleFragment.getView());
}
8、访问资源文件
@Test public void testResources() { Application application = RuntimeEnvironment.application; String appName = application.getString(R.string.app_name); String activityTitle = application.getString(R.string.title_activity_simple); assertEquals("LoveUT", appName); assertEquals("SimpleActivity",activityTitle); } |
四、BroadcastReceiver的测试
首先看下广播接收者的代码
public class MyReceiver extends BroadcastReceiver { @Override public void onReceive(Context context, Intent intent) { SharedPreferences.Editor editor = context.getSharedPreferences( "account", Context.MODE_PRIVATE).edit(); String name = intent.getStringExtra("EXTRA_USERNAME"); editor.putString("USERNAME", name); editor.apply(); } } |
广播的测试点可以包含两个方面,一是应用程序是否注册了该广播,二是广播接受者的处理逻辑是否正确,关于逻辑是否正确,可以直接人为的触发onReceive()方法,验证执行后所影响到的数据。
@Test public void testBoradcast(){ ShadowApplication shadowApplication = ShadowApplication.getInstance(); String action = "com.geniusmart.loveut.login"; Intent intent = new Intent(action); intent.putExtra("EXTRA_USERNAME", "geniusmart"); //测试是否注册广播接收者 assertTrue(shadowApplication.hasReceiverForIntent(intent)); //以下测试广播接受者的处理逻辑是否正确 MyReceiver myReceiver = new MyReceiver(); myReceiver.onReceive(RuntimeEnvironment.application,intent); SharedPreferences preferences = shadowApplication.getSharedPreferences("account", Context.MODE_PRIVATE); assertEquals( "geniusmart",preferences.getString("USERNAME", "")); } |
五、Service的测试
Service的测试类似于BroadcastReceiver,以IntentService为例,可以直接触发onHandleIntent()方法,用来验证Service启动后的逻辑是否正确。 public class SampleIntentService extends IntentService { public SampleIntentService() { super("SampleIntentService"); } @Override protected void onHandleIntent(Intent intent) { SharedPreferences.Editor editor = getApplicationContext().getSharedPreferences( "example", Context.MODE_PRIVATE).edit(); editor.putString("SAMPLE_DATA", "sample data"); editor.apply(); } } |
以上代码的单元测试用例:
@Test public void addsDataToSharedPreference() { Application application = RuntimeEnvironment.application; RoboSharedPreferences preferences = (RoboSharedPreferences) application .getSharedPreferences("example", Context.MODE_PRIVATE); SampleIntentService registrationService = new SampleIntentService(); registrationService.onHandleIntent(new Intent()); assertEquals(preferences.getString("SAMPLE_DATA", ""), "sample data"); } |
六、Shadow的使用
Shadow是Robolectric的立足之本,如其名,作为影子,一定是变幻莫测,时有时无,且依存于本尊。因此,框架针对Android SDK中的对象,提供了很多影子对象(如Activity和ShadowActivity、TextView和ShadowTextView等),这些影子对象,丰富了本尊的行为,能更方便的对Android相关的对象进行测试。
1.使用框架提供的Shadow对象
@Test public void testDefaultShadow(){ MainActivity mainActivity = Robolectric.setupActivity(MainActivity.class); //通过Shadows.shadowOf()可以获取很多Android对象的Shadow对象 ShadowActivity shadowActivity = Shadows.shadowOf(mainActivity); ShadowApplication shadowApplication = Shadows.shadowOf(RuntimeEnvironment.application); Bitmap bitmap = BitmapFactory.decodeFile("Path"); ShadowBitmap shadowBitmap = Shadows.shadowOf(bitmap); //Shadow对象提供方便我们用于模拟业务场景进行测试的api assertNull(shadowActivity.getNextStartedActivity()); assertNull(shadowApplication.getNextStartedActivity()); assertNotNull(shadowBitmap); } |
2.如何自定义Shadow对象
首先,创建原始对象Person
public class Person { private String name; public Person(String name) { this.name = name; } public String getName() { return name; } } |
其次,创建Person的Shadow对象
@Implements(Person.class) public class ShadowPerson { @Implementation public String getName() { return "geniusmart"; } } |
接下来,需自定义TestRunner,添加Person对象为要进行Shadow的对象(注:Robolectric 3.1 起可以省略此步骤)。
public class CustomShadowTestRunner extends RobolectricGradleTestRunner { public CustomShadowTestRunner(Class<?> klass) throws InitializationError { super(klass); } @Override public InstrumentationConfiguration createClassLoaderConfig() { InstrumentationConfiguration.Builder builder = InstrumentationConfiguration.newBuilder(); /** * 添加要进行Shadow的对象 */ builder.addInstrumentedPackage(Person.class.getPackage().getName()); builder.addInstrumentedClass(Person.class.getName()); return builder.build(); } } |
最后,在测试用例中,ShadowPerson对象将自动代替原始对象,调用Shadow对象的数据和行为
@RunWith(CustomShadowTestRunner.class) @Config(constants = BuildConfig.class,shadows = {ShadowPerson.class}) public class ShadowTest { /** * 测试自定义的Shadow */ @Test public void testCustomShadow(){ Person person = new Person("genius"); //getName()实际上调用的是ShadowPerson的方法 assertEquals("geniusmart", person.getName()); //获取Person对象对应的Shadow对象 ShadowPerson shadowPerson = (ShadowPerson) ShadowExtractor.extract(person); assertEquals("geniusmart", shadowPerson.getName()); } } |
七、关于代码
文章中的所有代码在此:https://github.com/geniusmart/LoveUT
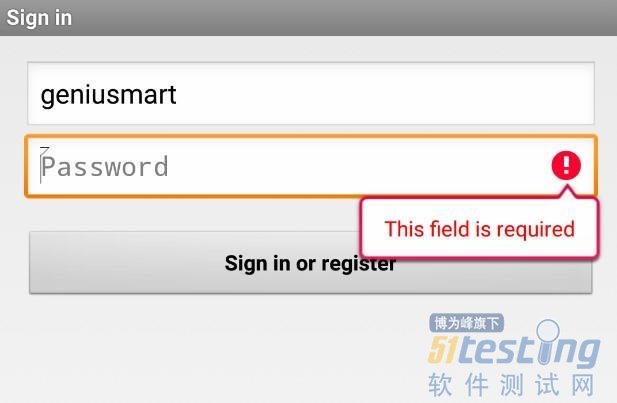
另外,除了文中所示的代码之外,该工程还包含了Robolectric官方的测试例子,一个简单的登录功能的测试,可以作为入门使用,界面如下图。
官方的登录测试DEMO