1. 概述
在理解了#7 介绍的HashMap后,我们来学习LinkedHashMap的工作原理及实现。首先还是类似的,我们写一个简单的LinkedHashMap的程序:
LinkedHashMap<String, Integer> lmap = new LinkedHashMap<String, Integer>();
lmap.put("语文", 1);
lmap.put("数学", 2);
lmap.put("英语", 3);
lmap.put("历史", 4);
lmap.put("政治", 5);
lmap.put("地理", 6);
lmap.put("生物", 7);
lmap.put("化学", 8);
for(Entry<String, Integer> entry : lmap.entrySet()) {
System.out.println(entry.getKey() + ": " + entry.getValue());
}
运行结果是:
语文: 1
数学: 2
英语: 3
历史: 4
政治: 5
地理: 6
生物: 7
化学: 8
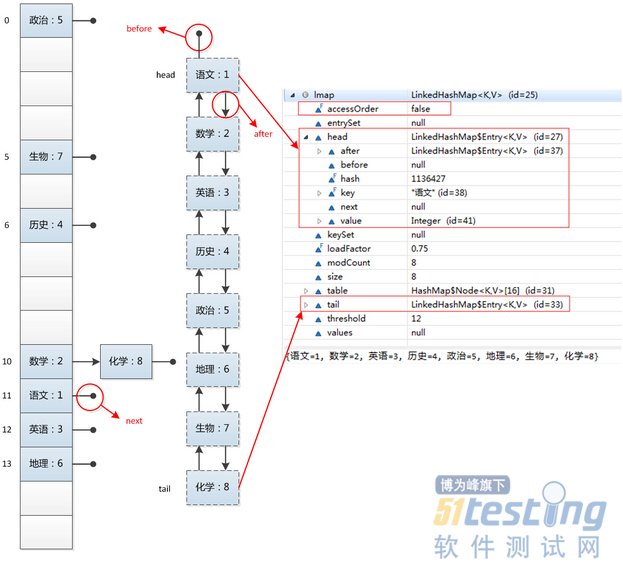
我们可以观察到,和HashMap的运行结果不同,LinkedHashMap的迭代输出的结果保持了插入顺序。是什么样的结构使得LinkedHashMap具有如此特性呢?我们还是一样的看看LinkedHashMap的内部结构,对它有一个感性的认识:
没错,正如官方文档所说:
Hash table and linked list implementation of the Map interface, with predictable iteration order. This implementation differs from HashMap in that it maintains a doubly-linked listrunning through all of its entries. This linked list defines the iteration ordering, which is normally the order in which keys were inserted into the map (insertion-order).
LinkedHashMap是Hash表和链表的实现,并且依靠着双向链表保证了迭代顺序是插入的顺序。
2. 三个重点实现的函数
在HashMap中提到了下面的定义:
// Callbacks to allow LinkedHashMap post-actions
void afterNodeAccess(Node<K,V> p) { }
void afterNodeInsertion(boolean evict) { }
void afterNodeRemoval(Node<K,V> p) { }
LinkedHashMap继承于HashMap,因此也重新实现了这3个函数,顾名思义这三个函数的作用分别是:节点访问后、节点插入后、节点移除后做一些事情。